Eco Friendly Home & Lifestyle, Home Decor Rural Livlihood, sling bag
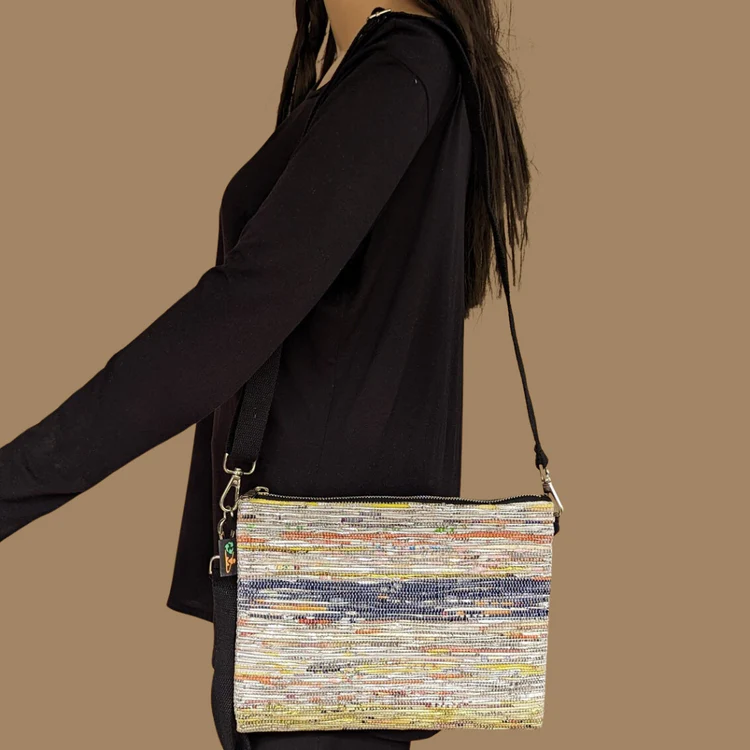
Shimmery Multicolored Upcycled Handwoven Sling Bag (SI0624-020) PS_W
₹900.0
Care Instructions:
- Spot clean with a damp cloth
- Avoid exposure to harsh chemicals
- Store in a cool, dry place
Embrace eco-friendly style with the Shimmery Multicolored Upcycled Handwoven Sling Bag. This unique and vibrant accessory is crafted from upcycled materials, giving discarded fabrics a new lease on life and reducing textile waste. Each bag is meticulously handwoven by skilled artisans, ensuring a one-of-a-kind design that stands out with its shimmering, multicolored pattern.
Features:
- Upcycled Materials: Made from repurposed fabrics, this bag contributes to reducing waste and promotes sustainable fashion.
- Handwoven Craftsmanship: Expertly handwoven by artisans, each bag showcases intricate patterns and textures, making every piece unique.
- Vibrant Design: The multicolored design adds a touch of sparkle and flair to any outfit, perfect for making a fashion statement.
- Sustainable Production: The handwoven process and use of upcycled materials result in a lower carbon footprint, supporting a more environmentally conscious lifestyle.
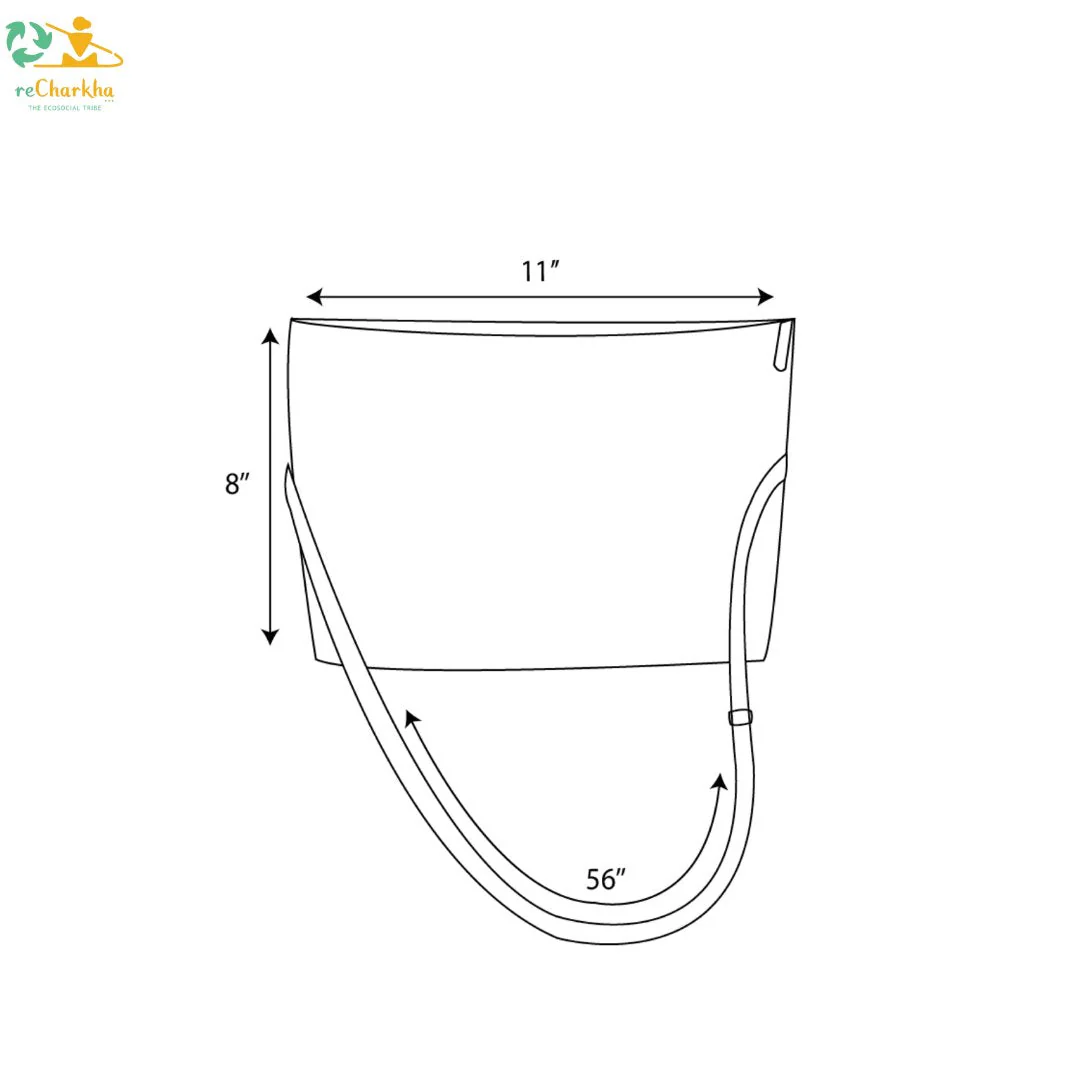
- Functional and Stylish: Designed for everyday use, the sling bag features ample space for essentials and a comfortable strap for easy carrying.
You must be logged in to post a review.
Q & A
Ask a question
There are no questions yet
1. Upcycling
Justification:- Upcycling refers to the process of repurposing waste materials or unwanted products into new items of higher value. By using discarded fabrics or materials, the production of this sling bag prevents waste from ending up in landfills.
- Upcycling reduces the need for virgin materials, which in turn lessens the environmental impact associated with extracting and processing raw materials. This helps to lower greenhouse gas emissions, energy consumption, and water usage. According to a study by the Journal of Cleaner Production, upcycling can significantly reduce carbon emissions compared to manufacturing new materials from scratch (Tucker & Rieckmann, 2017).
2. Handwoven Production
Justification:- The bag is handwoven, which typically involves less energy-intensive processes compared to mechanized manufacturing. Handweaving often uses traditional techniques that don't rely on large-scale machinery.
- Handwoven textiles often have a lower carbon footprint because they don't require extensive energy inputs for machinery and transportation. The International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment highlights that manual production methods generally have a lower environmental impact compared to automated processes (Hertwich & Peters, 2009).
3. Use of Sustainable Materials
Justification:- If the sling bag uses sustainable or eco-friendly materials, such as organic or recycled fibers, it further reduces its environmental impact.
- Using materials like organic cotton or recycled fibers generally requires less energy and water compared to conventional materials. For example, recycled polyester requires 75% less energy to produce than virgin polyester (Textile Exchange, 2016).
4. Reduced Waste
Justification:- Upcycling and handweaving contribute to reducing textile waste, which is a significant issue in the fashion industry.
- According to the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, the fashion industry is responsible for a significant portion of global waste and emissions. By recycling and upcycling materials, products help mitigate this issue by diverting waste from landfills and reducing the need for new raw materials (Ellen MacArthur Foundation, 2017).
5. Local Production
Justification:- If the sling bag is produced locally, it reduces the carbon footprint associated with transportation.
- Local production reduces the distance goods need to travel, which cuts down on transportation emissions. The Environmental Science & Technology journal emphasizes that transportation is a major contributor to the carbon footprint of products (Saxe & Larsen, 2004).
References:
- Tucker, M., & Rieckmann, T. (2017). Upcycling of textiles: An exploration of environmental benefits and potentials. Journal of Cleaner Production, 140, 235-245.
- Hertwich, E. G., & Peters, J. R. (2009). Carbon Footprint of Nations: A Global Assessment of Greenhouse Gas Emissions. International Journal of Life Cycle Assessment, 14, 73-82.
- Textile Exchange. (2016). Preferred Fiber & Materials Market Report.
- Ellen MacArthur Foundation. (2017). A New Textiles Economy: Redesigning Fashion’s Future.
- Saxe, H., & Larsen, H. F. (2004). Environmental impact of textile products. Environmental Science & Technology, 38(10), 2741-2747.
No more offers for this product!
General Inquiries
There are no inquiries yet.


















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.